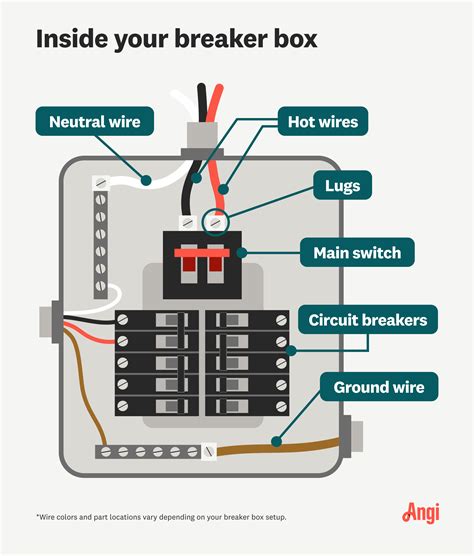
electrical breaker box neutral and ground The grounding conductor provides a safe path for the wayward electricity to flow back to the panel to trip the breaker and kill the power. Without the grounding wire, that misdirected electricity could shock you.
$5.98
0 · mixed ground and neutrals in breaker box
1 · grounding neutrals in breaker box
2 · grounding circuit breaker box
3 · grounded conductor in breaker box
4 · ground wiring for breaker box
5 · ground vs neutral wire breaker
6 · breaker box wiring neutral
7 · bonding neutral and ground in breaker box
Wrought iron, turned-wood and white vinyl porch railing are failproof picks to pretty up a traditional front porch; minimalist metal balusters (aka pickets) or stainless steel cable rails make a seamless addition to modern or contemporary abodes.
mixed ground and neutrals in breaker box
If you tie both neutral and ground to earth ground, or both to utility ground (AKA neutral), you have then defeated the purpose of having redundant grounding paths. You have in effect removed the fail safe by combining them and placing them on one leg/ground.Inside the panel there is only one bar with both ground and neutral wires .

king size 9-leg adjustable metal bed frame with headboard brackets
There are two bars because if it was used as a subpanel ground and neutral would . The NEC stipulates that neutral and ground wires be kept separate elsewhere in the home electrical system, including sub-pannels. This . Though a breaker box wiring neutral or ground is connected to the same bus bar, each serves a different purpose. A neutral wire has the ability .
The grounding conductor provides a safe path for the wayward electricity to flow back to the panel to trip the breaker and kill the power. Without the grounding wire, that misdirected electricity could shock you.You can connect the neutral and grounding wire to the neutral bus bar of a breaker box. The same rules apply whether you call it ‘Breaker Box’ or ‘Main Panel.’ The neutral and grounding conductors will only become a shock .
There are two bars because if it was used as a subpanel ground and neutral would have to be kept separated. The main breaker will cut power to the bus bars and breakers, but the lugs and feeder cables near the top of the panel will still .Neutral is the return path of the current, and ground wire holds the fault current to trip the breaker in protecting the person and the facility. The neutral and ground should never be bonded together in the facility except for the main panel.The neutral wire serves as a return path for electrical current while the ground wire provides a path for electrical current to earth. Since electricity flows from source to destination and back, each wire serves a specific need to ensure the .
If you tie both neutral and ground to earth ground, or both to utility ground (AKA neutral), you have then defeated the purpose of having redundant grounding paths. You have in effect removed the fail safe by combining them and placing them on one leg/ground. White: The neutral wire, responsible for sending unused electricity back into the breaker panel. Green : The ground wire, responsible for taking electricity back into the breaker panel and then into a rod buried in the ground—this prevents electrocution. The NEC stipulates that neutral and ground wires be kept separate elsewhere in the home electrical system, including sub-pannels. This separation protects your home and your family from dangerous situations should a ground fault occur. Though a breaker box wiring neutral or ground is connected to the same bus bar, each serves a different purpose. A neutral wire has the ability to return electricity to the panel breaker up to its power source, which is the transformer.
The grounding conductor provides a safe path for the wayward electricity to flow back to the panel to trip the breaker and kill the power. Without the grounding wire, that misdirected electricity could shock you.You can connect the neutral and grounding wire to the neutral bus bar of a breaker box. The same rules apply whether you call it ‘Breaker Box’ or ‘Main Panel.’ The neutral and grounding conductors will only become a shock hazard when you .There are two bars because if it was used as a subpanel ground and neutral would have to be kept separated. The main breaker will cut power to the bus bars and breakers, but the lugs and feeder cables near the top of the panel will still be hot.Neutral is the return path of the current, and ground wire holds the fault current to trip the breaker in protecting the person and the facility. The neutral and ground should never be bonded together in the facility except for the main panel.
The neutral wire serves as a return path for electrical current while the ground wire provides a path for electrical current to earth. Since electricity flows from source to destination and back, each wire serves a specific need to ensure the loop is maintained. F: Neutral bus. All ground and neutral (white) wires connect here. If you’re installing a standard breaker, the neutral (white) wire connects here, too. If you’re installing an arc-fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) breaker, you’ll connect the neutral to the breaker and run a “pigtail” wire to the neutral bus. G: Breaker space.If you tie both neutral and ground to earth ground, or both to utility ground (AKA neutral), you have then defeated the purpose of having redundant grounding paths. You have in effect removed the fail safe by combining them and placing them on one leg/ground.
White: The neutral wire, responsible for sending unused electricity back into the breaker panel. Green : The ground wire, responsible for taking electricity back into the breaker panel and then into a rod buried in the ground—this prevents electrocution. The NEC stipulates that neutral and ground wires be kept separate elsewhere in the home electrical system, including sub-pannels. This separation protects your home and your family from dangerous situations should a ground fault occur. Though a breaker box wiring neutral or ground is connected to the same bus bar, each serves a different purpose. A neutral wire has the ability to return electricity to the panel breaker up to its power source, which is the transformer.The grounding conductor provides a safe path for the wayward electricity to flow back to the panel to trip the breaker and kill the power. Without the grounding wire, that misdirected electricity could shock you.
You can connect the neutral and grounding wire to the neutral bus bar of a breaker box. The same rules apply whether you call it ‘Breaker Box’ or ‘Main Panel.’ The neutral and grounding conductors will only become a shock hazard when you .There are two bars because if it was used as a subpanel ground and neutral would have to be kept separated. The main breaker will cut power to the bus bars and breakers, but the lugs and feeder cables near the top of the panel will still be hot.Neutral is the return path of the current, and ground wire holds the fault current to trip the breaker in protecting the person and the facility. The neutral and ground should never be bonded together in the facility except for the main panel.The neutral wire serves as a return path for electrical current while the ground wire provides a path for electrical current to earth. Since electricity flows from source to destination and back, each wire serves a specific need to ensure the loop is maintained.
grounding neutrals in breaker box
grounding circuit breaker box
kitchen bath collection stainless steel under cabinet range hood
grounded conductor in breaker box
18-Gauge stainless steel: high-quality 18-gauge thickness and 300 series stainless steel for lasting durability. Quiet: sound-deadening pad(s) minimizes sound and vibration for a quieter time at the sink. U-channel installation: mounting clips placed inside the channel before installation mean less time under the sink for an easier install
electrical breaker box neutral and ground|grounding circuit breaker box