distribution possibilities box Pareto efficient allocation in the Edgeworth box: the slope of 2's indifference curve at an efficient allocation will equal the slope of 1's indifference curve; the points of tangency of the two curves. Salvaged used metal with wide corrugated pattern. Various natural and beautiful aged conditions and recycled aspects such as nail holes, dents & tears. All 30 .
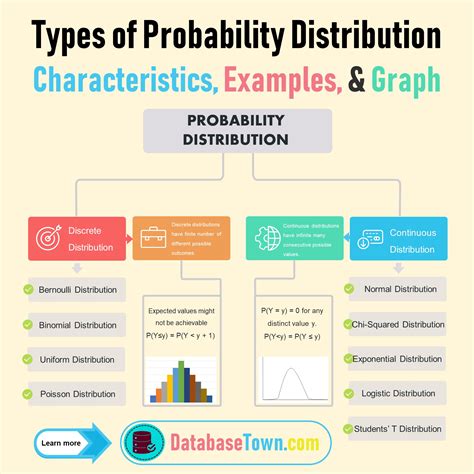
0 · Probability Distributions
1 · List of probability distributions
2 · Lecture Notes, Lecture 3 The Edgeworth Box
3 · Econ 101 Study Guide for First Exam
4 · Econ 101
5 · Distribution of objects into boxes
6 · Distribution Problems
7 · CONCEPTS OF EFFICIENCY
8 · 5.2: Discrete Probability Distributions
$7,490.00
Distribution Possibilities Box (DPB) A representation of how goods are distributed to individuals within a PPF. A point represents how much of each good will be given to each household.
Explain the concept of the consumption possibilities frontier (CPF) for an economy with one non-produced good and one produced good.
Probability Distributions
List of probability distributions
Graph showing output distribution between two individuals. Total revenue minus explicit costs only.Pareto efficient allocation in the Edgeworth box: the slope of 2's indifference curve at an efficient allocation will equal the slope of 1's indifference curve; the points of tangency of the two curves. A variable whose value depends upon a chance experiment is called a random variable. Suppose that a person is asked who that person is closest to: their mother or their . A probability distribution is an assignment of probabilities to all the possible values of the random variable. The abbreviation of pdf is used for a probability density (distribution) .
Question: In how many ways can $a$ objects be distributed into $b$ boxes taking into account all the possibilities (distinct and non-distinct) for both the objects and the boxes. ($a$ may be .The property that characterizes a distribution (occupancy) problem is that a ball (object) must go into exactly one box (bin or cell). This amounts to a function from balls to bins.The Lévy skew alpha-stable distribution or stable distribution is a family of distributions often used to characterize financial data and critical behavior; the Cauchy distribution, Holtsmark .How can we characterize a Pareto efficient allocation in the exchange Edgeworth box? When the shaded area of beneficial trades starting at this point vanishes Or when indifference curves for R and B through that point are mutually tangential
Distribution Possibilities Box (DPB) A representation of how goods are distributed to individuals within a PPF. A point represents how much of each good will be given to each household. Explain the concept of the consumption possibilities frontier (CPF) for an economy with one non-produced good and one produced good.Graph showing output distribution between two individuals. Total revenue minus explicit costs only.
Pareto efficient allocation in the Edgeworth box: the slope of 2's indifference curve at an efficient allocation will equal the slope of 1's indifference curve; the points of tangency of the two curves. A variable whose value depends upon a chance experiment is called a random variable. Suppose that a person is asked who that person is closest to: their mother or their father. The random variable of this experiment is the boolean variable whose possibilities are . A probability distribution is an assignment of probabilities to all the possible values of the random variable. The abbreviation of pdf is used for a probability density (distribution) function in your calculators. The probability distribution of X lists all the possible values of x and their corresponding probabilities.
Question: In how many ways can $a$ objects be distributed into $b$ boxes taking into account all the possibilities (distinct and non-distinct) for both the objects and the boxes. ($a$ may be greater than $b$ or may be less than $b$) There are 8 cases possible. CASE 1: All the objects are distinct and all the boxes are distinct.The property that characterizes a distribution (occupancy) problem is that a ball (object) must go into exactly one box (bin or cell). This amounts to a function from balls to bins.The Lévy skew alpha-stable distribution or stable distribution is a family of distributions often used to characterize financial data and critical behavior; the Cauchy distribution, Holtsmark distribution, Landau distribution, Lévy distribution and normal distribution are special cases.How can we characterize a Pareto efficient allocation in the exchange Edgeworth box? When the shaded area of beneficial trades starting at this point vanishes Or when indifference curves for R and B through that point are mutually tangential
Lecture Notes, Lecture 3 The Edgeworth Box
Distribution Possibilities Box (DPB) A representation of how goods are distributed to individuals within a PPF. A point represents how much of each good will be given to each household. Explain the concept of the consumption possibilities frontier (CPF) for an economy with one non-produced good and one produced good.Graph showing output distribution between two individuals. Total revenue minus explicit costs only.Pareto efficient allocation in the Edgeworth box: the slope of 2's indifference curve at an efficient allocation will equal the slope of 1's indifference curve; the points of tangency of the two curves.
A variable whose value depends upon a chance experiment is called a random variable. Suppose that a person is asked who that person is closest to: their mother or their father. The random variable of this experiment is the boolean variable whose possibilities are . A probability distribution is an assignment of probabilities to all the possible values of the random variable. The abbreviation of pdf is used for a probability density (distribution) function in your calculators. The probability distribution of X lists all the possible values of x and their corresponding probabilities.
Question: In how many ways can $a$ objects be distributed into $b$ boxes taking into account all the possibilities (distinct and non-distinct) for both the objects and the boxes. ($a$ may be greater than $b$ or may be less than $b$) There are 8 cases possible. CASE 1: All the objects are distinct and all the boxes are distinct.
The property that characterizes a distribution (occupancy) problem is that a ball (object) must go into exactly one box (bin or cell). This amounts to a function from balls to bins.

Econ 101 Study Guide for First Exam

Econ 101
Distribution of objects into boxes
Distribution Problems
5-Axis or More CNC Lathes. Used 2019 DOOSAN LYNX 2100 LYB 5-Axis CNC Lathe, machining length 20.1", max RPM 4500, 8" Samchully chuck, 3 live holders, 20 hp power, chip conveyor, tool presetter, and parts catcher. Ideal for h.
distribution possibilities box|CONCEPTS OF EFFICIENCY