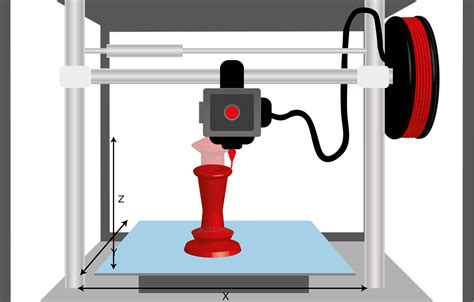
cnc additive and subtractive manufacturing Additive manufacturing is a process that builds parts from the base up by adding successive layers to manufacture a product. 3D printing is the technology . What is oil canning? Oil canning is an attribute of metal cladding, in particular it appears on panels that have been folded or roll formed from thin sheet metal. The appearance of oil canning can be minimised, but it is a characteristic of sheet metal roof and wall panel systems.
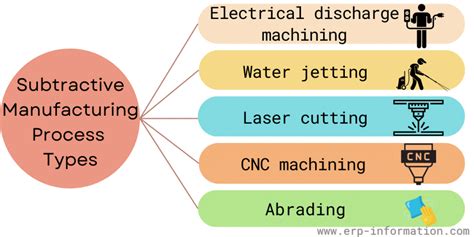
0 · types of subtractive manufacturing
1 · subtractive manufacturing techniques
2 · subtractive manufacturing pros and cons
3 · subtractive manufacturing in 3d printing
4 · disadvantages of subtractive manufacturing
5 · difference between subtractive and additive
6 · comparison of additive manufacturing processes
7 · additive manufacturing cost comparison
CNC machines have revolutionized modern manufacturing by providing a reliable, accurate, and efficient method of producing parts. Whether you’re building components for an airplane or crafting custom furniture, CNC machines can handle the job with ease and precision.
Explore the key differences, advantages, and applications of additive manufacturing and subtractive manufacturing. Discover when and how to use each method in various industries.
In the realm of modern manufacturing, CNC Subtractive Manufacturing (CSM) stands as the bedrock of precision, versatility, and top-notch surface quality. Conversely, Additive Manufacturing (AM) represents an exciting frontier for .There are two interesting methods used in manufacturing. These are additive manufacturing vs subtractive manufacturing. What makes them different from each other? How do these .In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of additive manufacturing versus subtractive manufacturing, comparing their processes, benefits, and applications. 1. Additive .Additive manufacturing is a process that builds parts from the base up by adding successive layers to manufacture a product. 3D printing is the technology .
Subtractive manufacturing continuously removes the material from the outer surface until it is converted into the required shape. In contrast, the additive approach creates the desired shape by adding layers of materials. Additive manufacturing is a process that adds successive layers of material to create an object, often referred to as 3D printing. Subtractive manufacturing, as the name suggests, is the opposite. Rather than adding .
Explore the key differences, advantages, and applications of additive manufacturing and subtractive manufacturing. Discover when and how to use each method in various industries.In the realm of modern manufacturing, CNC Subtractive Manufacturing (CSM) stands as the bedrock of precision, versatility, and top-notch surface quality. Conversely, Additive Manufacturing (AM) represents an exciting frontier for intricate designs, yet it faces limitations in industries that demand speed of manufacture, precision, material .
There are two interesting methods used in manufacturing. These are additive manufacturing vs subtractive manufacturing. What makes them different from each other? How do these methods affect the quality and cost of products? Let’s take a closer look at these methods.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of additive manufacturing versus subtractive manufacturing, comparing their processes, benefits, and applications. 1. Additive Manufacturing. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, involves building objects by adding material layer by layer.Additive manufacturing is a process that builds parts from the base up by adding successive layers to manufacture a product. 3D printing is the technology most associated with additive manufacturing. Subtractive manufacturing removes material to manufacture a part. Subtractive manufacturing continuously removes the material from the outer surface until it is converted into the required shape. In contrast, the additive approach creates the desired shape by adding layers of materials.
Additive manufacturing is a process that adds successive layers of material to create an object, often referred to as 3D printing. Subtractive manufacturing, as the name suggests, is the opposite. Rather than adding layers, subtractive manufacturing involves removing sections of a material by machining or cutting it away. Subtractive Manufacturing, like CNC machining, carves out masterpieces from raw materials. In contrast, Additive Manufacturing, or 3D printing, builds objects layer by layer. Each method has unique strengths and limitations, impacting everything from cost to quality.In this guide, we’ll be taking a closer look at the various additive and subtractive manufacturing techniques and applications to help you decide how to leverage them for your own processes.Comparing additive and subtractive manufacturing, discover the key differences, advantages, and challenges of CNC machining and 3D printing for modern production.
Explore the key differences, advantages, and applications of additive manufacturing and subtractive manufacturing. Discover when and how to use each method in various industries.In the realm of modern manufacturing, CNC Subtractive Manufacturing (CSM) stands as the bedrock of precision, versatility, and top-notch surface quality. Conversely, Additive Manufacturing (AM) represents an exciting frontier for intricate designs, yet it faces limitations in industries that demand speed of manufacture, precision, material .There are two interesting methods used in manufacturing. These are additive manufacturing vs subtractive manufacturing. What makes them different from each other? How do these methods affect the quality and cost of products? Let’s take a closer look at these methods.In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of additive manufacturing versus subtractive manufacturing, comparing their processes, benefits, and applications. 1. Additive Manufacturing. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, involves building objects by adding material layer by layer.
Additive manufacturing is a process that builds parts from the base up by adding successive layers to manufacture a product. 3D printing is the technology most associated with additive manufacturing. Subtractive manufacturing removes material to manufacture a part. Subtractive manufacturing continuously removes the material from the outer surface until it is converted into the required shape. In contrast, the additive approach creates the desired shape by adding layers of materials.
Additive manufacturing is a process that adds successive layers of material to create an object, often referred to as 3D printing. Subtractive manufacturing, as the name suggests, is the opposite. Rather than adding layers, subtractive manufacturing involves removing sections of a material by machining or cutting it away. Subtractive Manufacturing, like CNC machining, carves out masterpieces from raw materials. In contrast, Additive Manufacturing, or 3D printing, builds objects layer by layer. Each method has unique strengths and limitations, impacting everything from cost to quality.In this guide, we’ll be taking a closer look at the various additive and subtractive manufacturing techniques and applications to help you decide how to leverage them for your own processes.

types of subtractive manufacturing

concrete pier metal brackets
CNC-controlled lathes, mills and machining centers can be used to machine a wide variety of industrial and automotive parts. Most engine builders who have CNC equipment, however, use it primarily for engine block and .
cnc additive and subtractive manufacturing|types of subtractive manufacturing